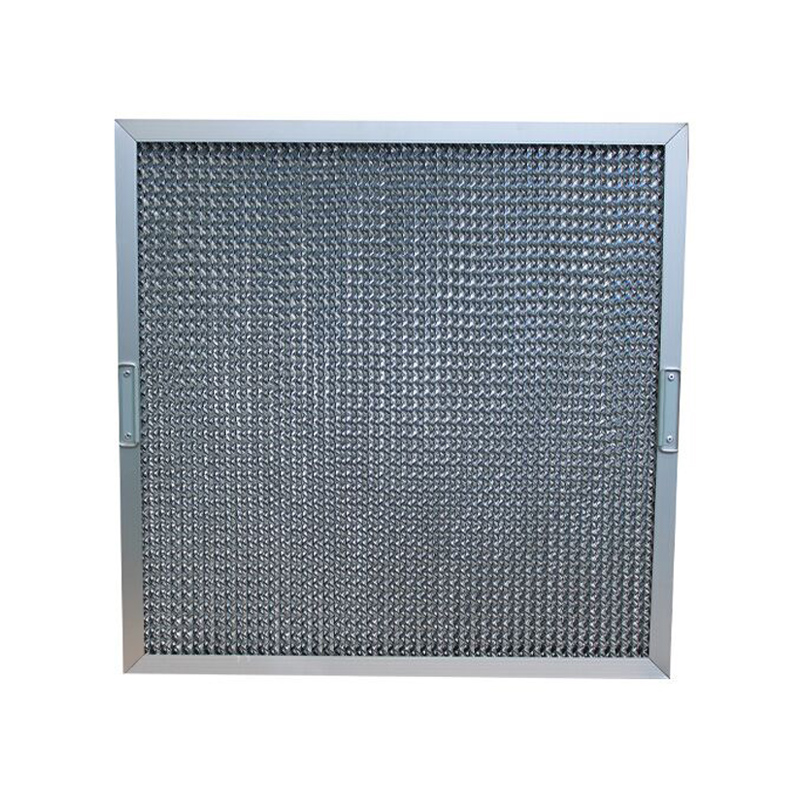
Introduction:
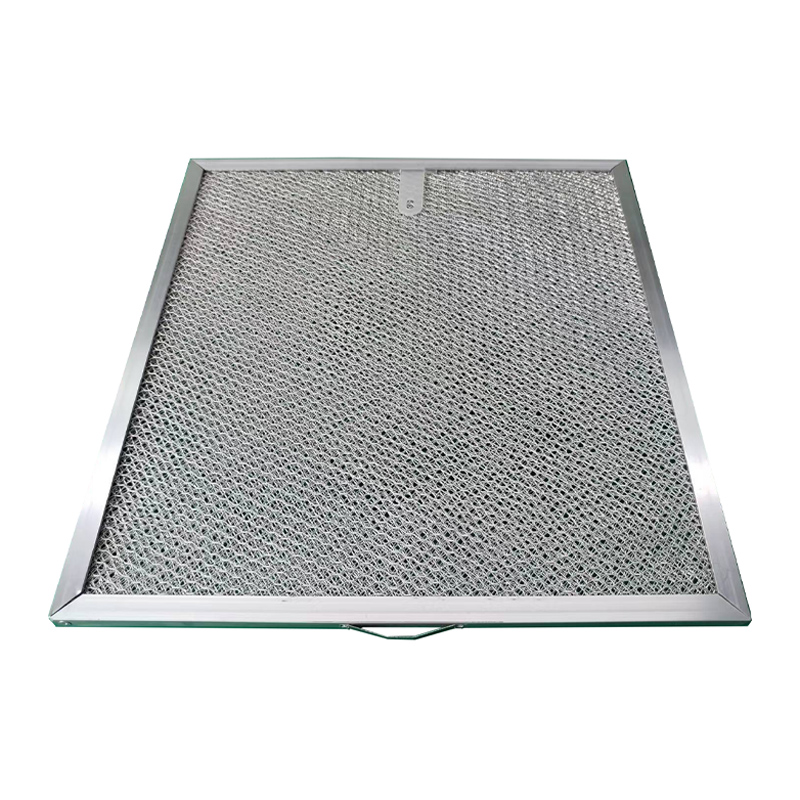
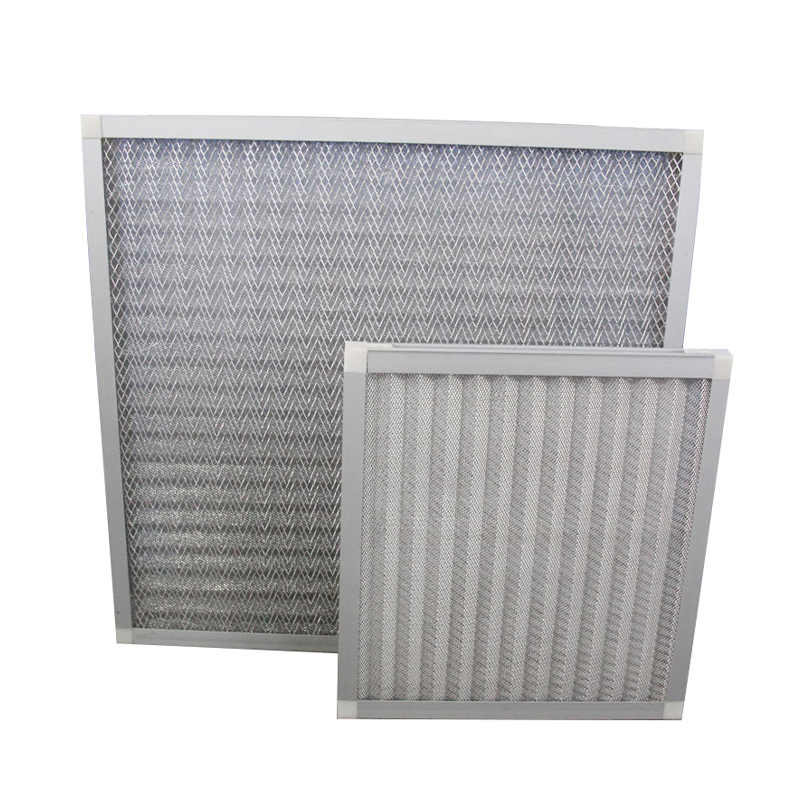
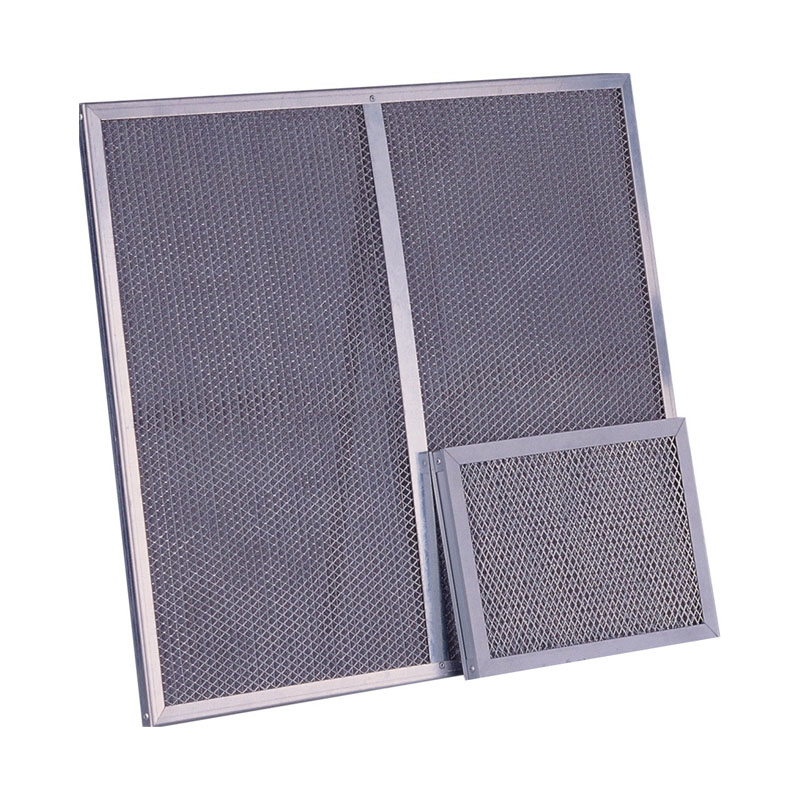
Metal mesh filters are mainly composed of different sizes of corrugated aluminium mesh, and staggered in the inner frame, which greatly reduces the gap between the aluminium mesh, thus providing a good filtration effect. Due to its multi-level filtering structure, it also increases the filtering area to a certain extent.
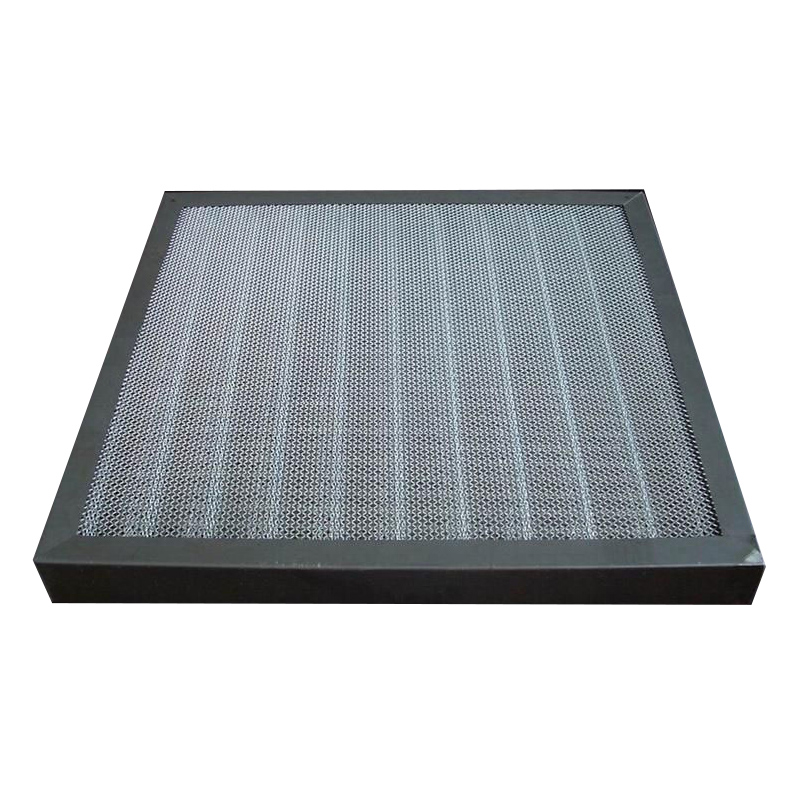
For acid, alkali or high temperature environment, stainless steel frame and stainless steel folded mesh can be used to ensure that the metal mesh filter can operate normally.
Use | Coarse dust filtration (for high temperature environments); pre-filtration of air filtration systems |
Type | Flat plate metal mesh filter |
Frame | Galvanised steel, aluminium alloy or stainless steel |
Filter media | Aluminium or stainless steel wire mesh |
Protective mesh | Aluminium or stainless steel wire mesh |
EN779 class | G2 |
Average weighing efficiency | 65%-80 % (ASHRAE 52.1-1992) |
Minimum Efficiency Reporting Values | MERV 2-5 (ASHRAE 52.1-1992) |
Final Resistance | (Recommended) 150 Pa - (Maximum) 250 Pa |
Maximum airflow | 125% of rated airflow |
Temperature Resistance | 250°C |
![Panel Metal Mesh Pre Filter Panel Metal Mesh Pre Filter]()
Common Sizes:
Size (mm) | Airflow (m3/h) | Efficiency Grade | Initial Resistance (Pa) | Recommended Final Resistance (Pa) |
295*595*46 | 1800 | G4 | ≤45 | ≤220 |
595*595*46 | 3600 |
Different air volumes at different wind speeds. Special sizes and specifications can be made according to customer requirements. |
Applications:
Metal mesh filters are generally applicable to coarse dust filtration systems for air conditioning in high-rise buildings, primary filtration for industrial-grade air ventilation equipment, as well as ventilation systems requiring resistance to acid and alkali and high temperature, and wax spraying filtration in automobile assembly workshops.
Cleaning and maintenance:
The cleaning and maintenance of metal mesh filters can be carried out using physical and chemical methods based on the pollution situation and the chemical properties of the pollutants.
The physical methods for cleaning can include clean liquid backwashing, clean gas backwashing, and ultrasonic methods.
Chemical cleaning methods include dilute acid, dilute alkali, oxidants, surfactants, enzymes, and other methods.
The decarbonization and filtration in the pharmaceutical and chemical industries often require the use of back blowing and backwashing methods combined with ultrasonic cleaning, which can achieve better results. The water industry generally uses 5% nitric acid immersion to achieve cleaning effects due to the presence of water-soluble salts and oxides on the surface of filter cartridges.